How the Internet Works🕸️ and Connects to Our Daily Lives 🚩?
Understanding the Reality Behind the Magic🪄 of Connectivity 🚀
Why use the internet ?
The basic idea is sending a file from one user to another. The process looks simple: you write a message, click the send button, and the other person gets the message. But behind the scenes, the internet isn’t magic—it uses some rules and steps to make sure the message is sent safely and quickly. that internet use one model that is OSI model.
OSI Model ( Open System Interconnection )
This is the model that use to communicate the devices this is the 7 Layer the every layar work specific task
Physical Layer
The cable connecting your computer to the internet works at this layer.
Data Link Layer
Your Wi-Fi router uses this layer to communicate with your phone or laptop.
Network Layer
Like Google Maps for data, it finds the best route for sending your message.
Transport Layer
When you download a file, this layer ensures the file is complete without missing parts. and this is help of achived using TCP & UDP model
Session Layer
When you're in an online video call, this layer ensures the connection stays active.
Presentation Layer
If you watch a YouTube video, it’s compressed so it loads faster.
Application Layer
When you open a website using a browser, this layer is used.

TCP & UDP ( Transport Layer)
TCP (Transmisson Control Protocol)
TCP helps with the transmission of data packets without loss and maintains order, making it the most reliable. It uses a 3-way handshake to establish the connection before sending data.
Working Flow of 3-Way Handshake

Client → Server :
- The client sends a SYN(Synchronize) packet to the server to start a connection.The packet includes a randomly generated sequence number to identify the start of the communication.
Server → Client :
- The server responds with a SYN-ACK packet.The SYN part indicates the server is ready to communicate, and the ACK(Acknowledge) part acknowledges the client's initial sequence number.
Client → Server :
- The client sends an ACK packet back to the server to confirm it received the server’s sequence number.
Then they create the actual established connection that is most reliable.
UDP ( User Datagram Protocol)
UDP is like sending a postcard. It’s faster but less reliable, and there’s no guarantee it will reach its destination.But still, some use cases exist that use UDP because faster transmission is required.Like Video Calls, Voice Calls etc.
TCP VS UDP
Feature | TCP | UDP |
Reliability | Reliable, resends lost data | Unreliable, no resending |
Connection | Connection-oriented | Connectionless |
Speed | Slower due to error checking,3-way handshake | Faster, no error checking,no handshake |
Use Cases | Whatsapp chat, email, file transfer | Video streaming, gaming, VoIP |
Every file transfer uses specific protocols (rules) to ensure data is sent and received properly. To establish a connection, the destination's IP address is required. An IP address acts like the address of your home, but for digital devices on a network. It uniquely identifies each device and helps locate it over the internet. The IP address also plays a crucial role in mapping to the DNS (Domain Name System), which translates human-readable domain names (like example.com) into the IP addresses that computers use to communicate. and help also Root server.
Works on the DNS help of diagram :
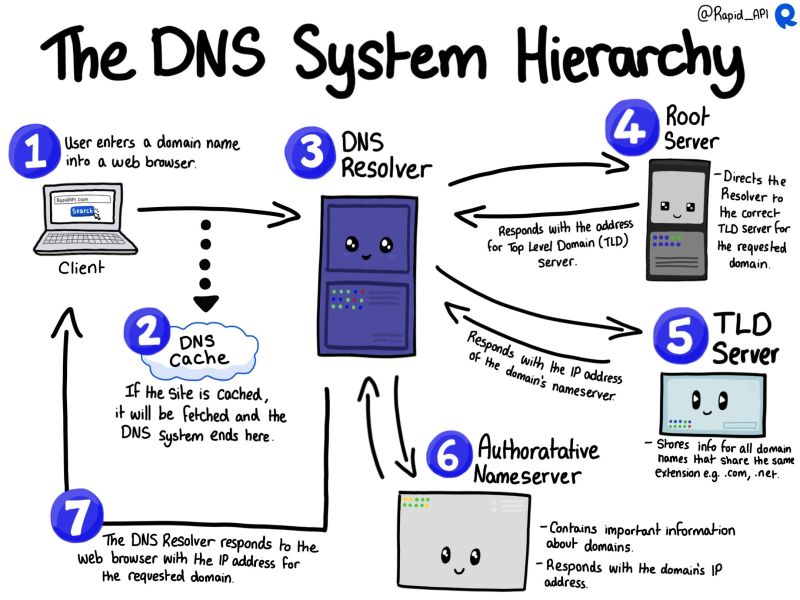
This is the working flow... Thank you for visiting and reading my article.😀
